KMP算法
KMP算法:查找连续子串,返回值:str1中str2开始的位置/-1
例:str1:ABCD1234de
str2:1234 返回值:4
str3:1234e 返回值:-1
暴力解法:遍历str1,看每个开头能否配出str2
时间复杂度:O(mn)
KMP算法基础:next数组
——str2中每个字符对应一个信息:最长公共前后缀(该字符前面的字符串相等前缀和后缀的最大长度,并且不能取到整体)
例:abbabb k k==>3
| 长度 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
| 前缀 |
a |
ab |
abb |
abba |
abbab |
不讨论 |
| 后缀 |
b |
bb |
abb |
babb |
bbabb |
|
|
!= |
!= |
== |
!= |
!= |
|
所以str2对应一个next arr==》用来加速匹配过程
例:str2={a,a,b,a,a,b,s}
next={-1,0,1,0,1,2,3} ps:next[0]=-1(人为规定),next[1]=0
KMP算法实现原理
——目的:让i跳的尽可能快(经典:i=i+1)
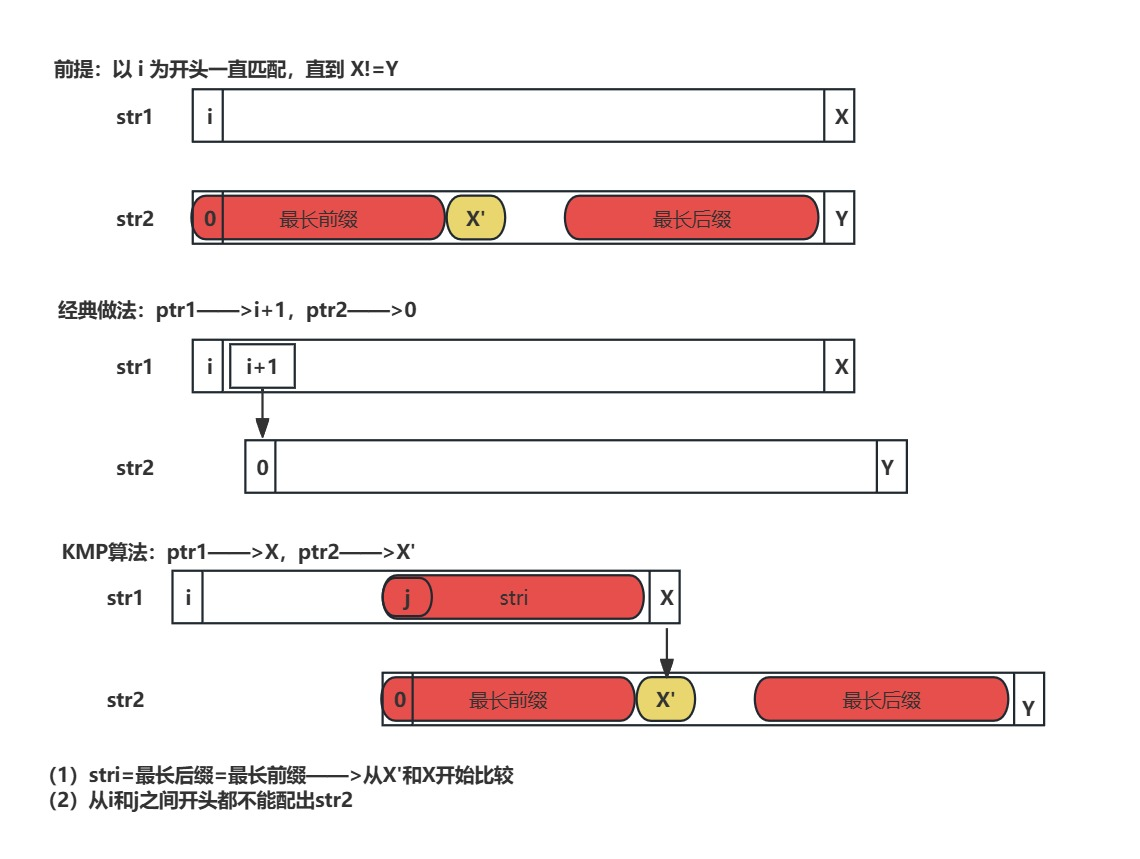
(2)的证明通过反证法:设k在i~j之间,k开始能配出str2……推出跟最长公共前后缀矛盾
next数组的求法
求next[i]
找next[i-1]==》前缀的下一位?=next[i-1]
相等:next[i]=next[i-1]+1
不相等:cur再往前跳,来到cur对应前缀的下一位(next[cur]),判断跟str[i-1]是否相等
完整代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
| #include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
vector<int> getNextArray(string str) {
int size = str.size();
if (size == 1) {
return { -1 };
}
vector<int> next(size);
next[0] = -1;
next[1] = 0;
int i = 2;
int cur = 0;
while (i < size) {
if (str[i - 1] == str[cur]) {
next[i++] = ++cur;
}
else if (cur > 0) {
cur = next[cur];
}
else {
next[i++] = 0;
}
}
return next;
}
int KMP(string str1, string str2) {
if (str1.empty() || str2.empty() || str1.size() < str2.size()) {
return -1;
}
vector<int> next = getNextArray(str2);
int ptr1 = 0, ptr2 = 0;
while (ptr1 < str1.size() && ptr2 < str2.size()) {
if (str1[ptr1] == str2[ptr2]) {
ptr1++;
ptr2++;
}
else if (ptr2 == 0) {
ptr1++;
}
else {
ptr2 = next[ptr2];
}
}
return ptr2 == str2.size() ? ptr1 - ptr2 : -1;
}
int main() {
string str1 = "abcd1234";
string str2 = "1234";
string str3 = "1234e";
cout << KMP(str1, str2) << endl;
cout << KMP(str1, str3);
}
|
